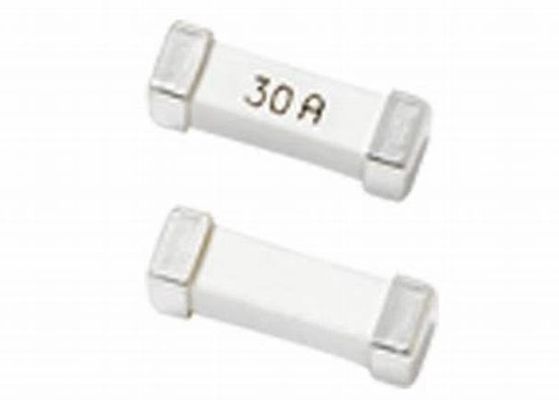
5.2x20mm Fast Acting Ceramic Tube Fuse 250VAC 3A With Alloy Element Nickel Plated Brass Cap For Big Current Application
Description
AOLITTEL Ceramic Tube Fuse is suitable for various kinds of electronic devices’ circuit over current protection. Widely used in industrial of Lighting, Power supply and Adapter applications, etc.Used as supplementary protection in appliance or utilization equipment to provide individual protection for
components or internal circuits.
___________________________________________________________ Download________
Download________
Dimension (mm)


|
NO.
|
Part Name
|
Material
|
| 1 |
Cap
|
Nickel Plated Brass
|
| 2 |
Body
|
Ceramic Tube
|
| 3 |
Fuse element
|
Alloy
|
| 4 |
Lead
|
CP Wire
|
Specification
A=250V,B=125V
|
P//N
|
Ampere
Rating
|
Voltage
Rating
|
Breaking
Capacity
|
I2TMelting
Integral(A2.S)
|
Agency Approvals
|
| UL |
cUL |
PSE
|
| 5.250BFC0100A/B |
100mA |
250V/125V |
10000A@125 V AC (200mA~10A);
35A@250V AC (200mA~1A);
100A@250V AC (1.25A~3.5A);
200A@250V AC (4A~10A).
|
0.002 |
○ |
○ |
○ |
| 5.250BFC0125A/B |
125mA |
250V/125V |
0.003 |
○ |
○ |
○ |
| 5.250BFC0160A/B |
160mA |
250V/125V |
0.005 |
○ |
○ |
○ |
| 5.250BFC0200A/B |
200mA |
250V/125V |
0.01 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC0250A/B |
250mA |
250V/125V |
0.02 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC0300A/B |
300mA |
250V/125V |
0.04 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC0315A/B |
315mA |
250V/125V |
0.045 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC0350A/B |
350mA |
250V/125V |
0.055 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC0400A/B |
400mA |
250V/125V |
0.07 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC0500A/B |
500mA |
250V/125V |
0.1 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC0630A/B |
630mA |
250V/125V |
0.2 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC0750A/B |
750mA |
250V/125V |
0.35 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC0800A/B |
800mA |
250V/125V |
0.45 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC1100A/B |
1A |
250V/125V |
0.9 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC1125A/B |
1.25A |
250V/125V |
1.3 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC1150A/B |
1.5A |
250V/125V |
1.6 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC1160A/B |
1.6A |
250V/125V |
2.5 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC1200A/B |
2A |
250V/125V |
5.8 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC1250A/B |
2.5A |
250V/125V |
7.6 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC1300A/B |
3A |
250V/125V |
8.1 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC1315A/B |
3.15A |
250V/125V |
11 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC1350A/B |
3.5A |
250V/125V |
19 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC1400A/B |
4A |
250V/125V |
28 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC1500A/B |
5A |
250V/125V |
40 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC1600A/B |
6A |
250V/125V |
50 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC1630A/B |
6.3A |
250V/125V |
64 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC1700A/B |
7A |
250V/125V |
107 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC1800A/B |
8A |
250V/125V |
133 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC2100A/B |
10A |
250V/125V |
242 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC2150A/B |
15A |
250V/125V |
368 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC2200A/B |
20A |
250V/125V |
442 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC2250A/B |
25A |
250V/125V |
568 |
● |
● |
○ |
| 5.250BFC2300A/B |
30A |
250V/125V |
715 |
● |
● |
○ |
So, What Exactly is causing that Blown Fuse?
Electrical wiring and systems that were installed up until a decade ago were quite different from the ones used today; and there was a specific reason for this. The types of electrical equipment and appliances used at that point of time were vastly different from the ones used today and their power requirements weren’t as demanding. However, things are different now; and current day appliances are power hungry.
This adds to the load on the wiring in your home or commercial establishment. If you have older wiring and other systems on your property, chances are that you have the older-style ceramic fuses as well- and you’ll find they blow very often. So why exactly does a fuse blow?

Blown fuse- how it occurs
Most people wonder why the fuses on their property, frequently keep blowing. The electricity that is directed to your property through the main lines, comes in at a particular strength and under normal circumstances, this electricity should also flow smoothly through the system without too much of resistance. Smaller equipment and appliances such as irons etc. operate on lower amperage while the larger equipment such as washing machines, dishwashers and the like, require much higher amperage.
When different equipment is plugged into the powerpoints in your home and are being operated simultaneously, they create a certain amount of resistance in the wiring. The fuses that are factored into each circuit are specifically-designed to bear certain amperage and prevent the electrical wiring from getting overheated.
When excessive power gets pulled in by the system, the wire inside the fuse melts and causes a break and the electricity in that circuit gets cut-off; this is referred to as a blown fuse. In essence, the fuse is like a sentry or a safety device that stops excessive power from flowing through the system and prevents fires from erupting on your property.
Blown fuses- the reasons
As mentioned earlier, when any appliances pulls in more amperage than what the circuit can handle, it results in a build-up of heat and causes blown fuse
If temporary overages occur in quick succession, they slowly cause the filament to weaken and you may have to deal with a blown fuse even if the amperage in a particular circuit hasn’t been exceeded.
You will find different types of fuses- while some of them are specifically built to bear a series of overloads before they blow, others are much more fragile and even as single power surge will cause them to blow. One of the first things to do in case of a blown fuse is to systematically unplug all the appliances and devices from that circuit and then install the new fuse.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!