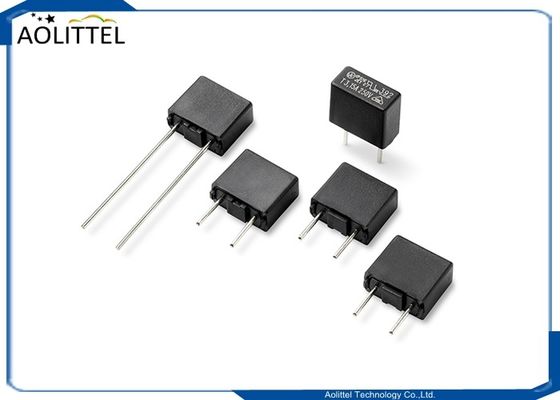
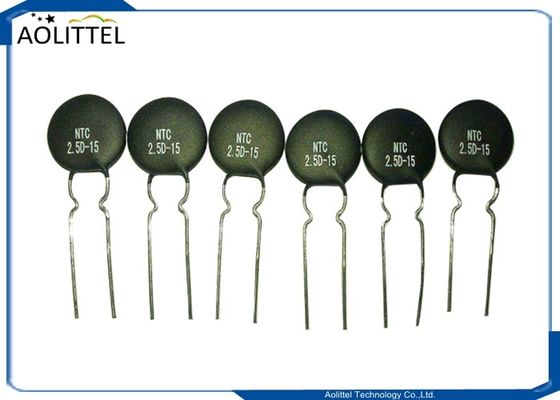
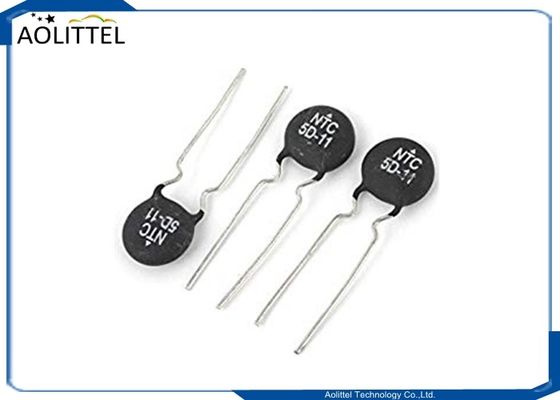
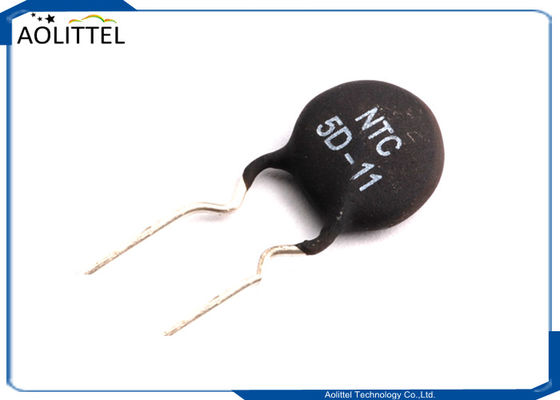
5 Ohm 4A Through Hole Power NTC Thermistor Surge Current Limiting MF72-5D-11 7.5mm Lead Spacing
Description
* The NTC thermistors are reliable and stable, with wide range of over-current control.
* With small size and large power, they have strong capacity to inhibit surge current.
* Large material constant (B value), with small residual resistance.
* Thermal shock resistance, with wide range of operating temperature.
* Used for controlling the inrush current of motor, heaters, bulb voltage Stabilizer, electronic energy-saving lamp, electronic Rectifier and other electronic installations.
Note: The thermistor cannot be used in parallel in the circuit.
Specification
* Product Name: NTC Thermistor
* Color: Black, Silver Tone
* Material: Ceramic, Metal
* Model: 5D-11
* Zero Power Resistance @25C: 5 Ohm
* B Value: >/=2700
* Thermal Recovery Time Coefficient: 45s
* Thermal Dissipation Constant: 13mw/C
* Operating Temperature: -50-200C
* Max Steady State Current: 4A
* 25C Insulation Max Resistance: </= 0.139 Ohm
* Lead Type: Radial Direction
* Lead Shape: Informing
* Pin Pitch: 7.5mm
* Lead Size(Approx.): 0.7 x 25mm / 0.03 x 1inch (D*L)
* Body Size(Approx.): 11 x 4.8mm / 0.43 x 0.19inch (D*T)
| Part Number |
Resistance @25℃
R25
(Ω) |
Max.
Stable
Current
(A) |
Approx.
Resistance
at max.
current
(Ω) |
Dissipation
Factor
(mW/℃) |
Thermal
Time
Constant
(S) |
Operating
Temperature
(℃) |
|
|
5 |
4 |
0.156 |
13 |
45 |
.-55℃~200℃ |



How do you choose the right type of NTC Thermistor to limit inrush current for capacitive applications?
Inrush current refers to the maximum, instantaneous input current drawn when power is applied to an electronic system’s power supply. A dc system has an input capacitor and an ac input system has and input rectifier and capacitor that can exhibit high inrush currentwhen the associated equipment turns on. If steps are not taken to minimize this inrush current, it can damage power devices and reduce equipment life. A safe and cost effective way to reduce inrush current is to use an inrush current limiter (surge limiter), which is a special type of negative temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistor.
Inrush current occurs at the moment the power switch is thrown. This happens because the input filter capacitor acts as a short and its minimum equivalent series resistance (ESR) and line resistance are only a few milliohms, which can lead to a high inrush current.
Four factors can affect inrush current:
- Energy of the inrush current
- Minimum resistance required by the NTC thermistor (at t = 0)
- Steady-state current
- Ambient temperature
We’ll present the details of these four items. First we will look at the energy of the inrush current, which is caused by input capacitors expressed as:

(Equation 1)
Where:
E = Energy of the inrush current
C = Capacitance value (F)
VPEAK= Resultant peak voltage
The minimum resistance required by the NTC thermistor will vary from one application to another, depending on the line voltage, peak inrush current, and the desired inrush current limitation due to fuse and circuit breaker ratings. As a rule of thumb, if the maximum allowable inrush current is not known, either the diode bridge specifications or the oscilloscope readings of the inrush current will dictate the minimum resistance required by the NTC thermistor. Typically, one third of the observed inrush current from the oscilloscope readings is acceptable.
For Example:

(Equation 2)
Where:
RMIN = Minimum resistance required by the NTC thermistor at t = 0 and temperature = 25 ºC
ILIMIT = Desired inrush current limit
The operating current must be at or below the steady-state current rating of the NTC thermistor.
The maximum steady-state current can be found by:

(Equation 3)
Where:
IMAX = Maximum steady-state current
Output power = Output power of the transformer
Efficiency = Efficiency of the transformer
Input voltage = Minimum input voltage
In some applications, the NTC thermistor is bypassed with a timed relay after the inrush current. Even though the thermistor is out of circuit during operation, it is best to select a thermistor that can handle steady-state current in case the relay fails.
Ambient temperature will dictate if there is a need for:
- De-rating of resistance
- De-rating of steady-state current
The rated resistance of the NTC thermistor is at 25 ºC, so de-rating of the resistance rating will be needed for ambient temperatures above 25 ºC, as the resistance of the thermistor will be lower. Ametherm (resistance/Time) R/T curves will dictate how much de-rating is needed.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!