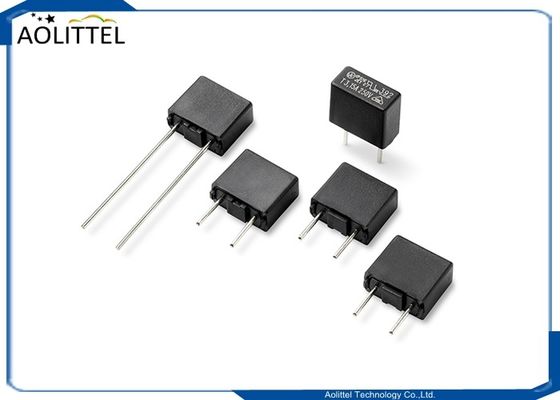
Standard PCB Mount Quick Insert Nylon Stackable Medium ATC ATO Auto Fuse Holder Block For Plug-in Automotive Fuse 1A-30A
Dimension (mm)
Description
Pre-assembled fuse holders to accomodate mini, standard and maxi blade fuse sizes. Easily mounted and soldered to the PCB,the mini size holder is compatible with ATO 297 and ATM automotive blade fuses. The standard size holder is compatible with ATO 257 and Bussman ATC automotive blade fuses. The maxi size holder is compatible with Maxi 297 and Max series fuses. holders mount vertically on the PCB.

Application
Fuseholder for 42V PowerNet with coding for TAC fuses-links. Attachable in X - direction. Rated voltage 58V; crimp terminals
Fuseholder for ATO / FKS size fuses-links. Attachable in X - direction. Rated voltage 80V; crimp terminals.
Fuseholder for ATO / FKS size fuses-links. 90° bended solder-able tin plated contacts. Rated voltage 80V.
Recommend Auto Blade Fuse

Specifications
| Insertion & Extraction Force |
1 Kg. Min |
| Dielectric Strength For 60 Seconds |
AC 1500V Min |
| Suitable Rated Current |
30A Max. |
| Insulation Resistance At 500v DC |
100M Min. |
| Temperature Rise |
50 Max. |
| Body Material |
Nylon With Glass Fiber |
| Voltage Drop |
20mV Max |
| Terminals |
Brass Tin Plated |
| P.C Board Snap-In Type |
WGP20,WGP29; |
| P.C BOARD Quick Insert Terminal Type |
#WGP21,#WGP22,#WGP23,#WGP24,#WGP25,
#WGP26,#WGP27,#WGP28,#WGS01,#WGS02;
|
More Models
|
WGP20 ATC Fuse Holder

|
WGP21 Auto Fuse Holder

|
WGP22 Medium Blade Fuse Holder

|
|
WGP23 Medium Auto Fuse Holder

|
WGP24 Automotive Fuse Holder

|
WGP25 Car Fuse Holder

|
|
WGP26 Auto Fuse Clip

|
WGP27 Auto Fuse Block

|
WGP28 Mini Blade Fuse Holder

|
|
WGP29 Blade Fuse Holder

|
|
|
KNOW YOUR FUSES

In order to select the proper protective device, the following parameters and criteria need to be considered:
1. What is the normal operating current of the circuit?
2. What is the operating voltage?
3. Is the circuit AC or DC?
4. What is the operating ambient temperature?
5. Is the device being used for short-circuit
protection, over-load protection, or both?
6. What are the physical size limitations?
7. Does the fuse need to be "field-replaceable"?
8. Is resettability an issue?
9. How will I mount the device?
10. What are the cost considerations?
How will the fuse be mounted?
One of the most careful considerations that need to be made is the mounting of the fuse in the circuit. There are several options at hand:
1. Direct Solder: In this method, the fuse is directly soldered into or onto the printed circuit board (PCB). The drawback to this design is the lack of field replaceable parts as discussed in great detail in the above section but cost can be significantly reduced with this mounting method.
2. Fuse Clips: Fuse clips are relatively inexpensive and allow for field replaceability. Fuseclips are typically mounted on a PCB so any attempt at replacing the fuse will require opening of the piece of equipment by the end-user. Additionally, removing a fuse from a fuse clip without disconnecting the power source could lead to an electrical shock when touching the fuse. Fuse clips are available for all "tube" fuses as well as microfuses. Typically fuseclips are limited to 20A of normal current (also available in 30A). Fuse clips are generally not listed or recognized by any safety agencies.
3. Panel Mounted Fuseholders: Panel mounted fuseholders allow for easy access for the end-user to replace the fuse in the field. The panel mount fuseholder is shock-safe meaning that the fuse is removed safely when the cap of the fuseholder is removed preventing the possibility of electrical shocks. Fuseholders are typically tested and approved by safety agencies such as UL and CSA. Fuseholders are typically available up to 30A.
4. Fuse Blocks: Fuse blocks are like fuse clips however they do not need to be mounted on the PCB. Fuses mounted in fuse blocks are typically only accessible by opening the piece of equipment which could lead to electrical shocks if the equipment is not disconnected from the power source. Fuse blocks are one of the few methods to mount fuses of large amperage. 5. Inline Fuse Holders: Inline fuse holders are typically used as a part of a wire harness assembly or where no surface is available to secure another type of fuse mount. Inline fuse holders are generally available up to 100A in lower voltage applications and up to 30A in higher voltage applications.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!