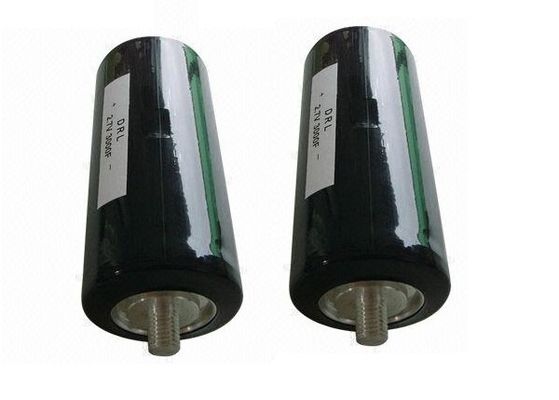
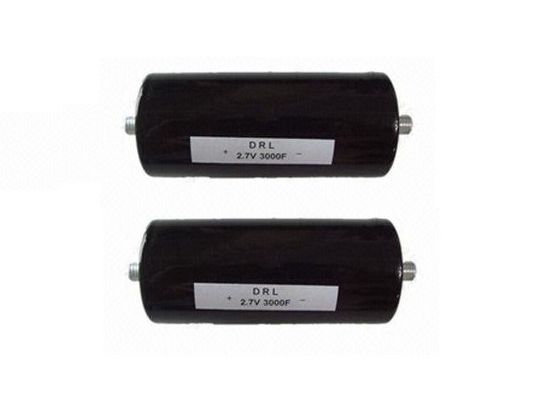
EDLC Electric Double Layer Capacitor 2.7V 3000F Super Capacitors With Threaded Terminal Low ESR Ultracapacitors
Electric Double Layer Capacitor (EDLC)
Ultracapacitor Cell Capacitance: 3000.0 F -10/+20%
Voltage: 2.7V
Dimensions: L = 138mm, OD = 60.7mm
Temperature Range: -40°C to +65°C
Features: 2.7V operating voltage Ultra low internal resistance Over 1 million duty cycles Threaded terminal Applications: Backup power Grid Stabilization Transportation Automotive subsystems Rail system power
___________________________________________________________ Download________
Download________
Description
PowerStor supercapacitors are unique, ultra-high capacitance devices utilizing electrochemical double layer capacitor (EDLC) construction combined with high-performance materials. This combination of advanced technologies allows Eaton to offer a wide-variety of capacitor solutions tailored to specific applications. The DRL60 series supercapacitor cells offers high-energy and power in a standardized form factor. Terminal design is optimized for high-reliability and low-contact resistance.
Dimension (mm)

| Size Code |
DxL |
D+/-0.2mm |
L+3mmmax |
H+/-0.5mm |
H2+/-0.5mm |
| 61E |
60x138 |
60 |
138 |
14 |
12 |
Features
Energy capture and re-use (Hybrids) for automotive, trucks, mining, construction, equipment, and cranes
Remote power for sensors, LEDs, switches
Long life energy storage, up to 20 years
Ultra-low-ESR for very-high-power density
Wide-operating temperature range
Maintenance free
Cost effective backup power and large energy recapture
Low-operating costs
High-efficiency (>98%) under broad environmental conditions
High-reliability, green solution
Application
Backup power
Peak power shaving, pulse power
Engine starting
Energy capture and re-use (Hybrids) for automotive, trucks, mining, construction, equipment, and cranes
Remote power for sensors, LEDs, switches
Ratings
| Capacitance |
3000 F to 3400 F |
| Maximum working voltage |
2.70 V / 2.85 V |
| Surge voltage |
2.85 V / 3.00 V |
| Capacitance tolerance |
0% to +20% |
| Operating temperature range |
-40 °C to +65 °C |
| Extended operating temperature range |
-40 °C to +85 °C (with voltage
derating to 2.30 V / 2.45 V @ +85 °C)
|
Characteristics
Standard atmospheric conditions
Unless otherwise specified, the standard range of atmospheric conditions for making measurements and tests is as follows:
Ambient temperature: 15°C to 35°C
Relative humidity : 25% to75%
Air Pressure : 86kPa to 106kPa
If there is any doubt about the results, measurement shall be made within the following conditions:
Ambient temperature: 20°C ± 2°C
Relative humidity : 60% to 70%
Air Pressure : 86kPa to 106kPa
Operating temperature range
The ambient temperature range at which the capacitor can be operated continuously at rated voltage
is -40°C to 60°C.
LET'S LEARN ABOUT SUPER CAPACITORS! (A PRACTICAL GUIDE TO SUPER CAPACITORS)

THEORY
Super capacitors act like any other kind of capacitor, only they can store tremendous amounts of energy. Many capacitors that you'd have seen in audio circuits have capacitances such as 470uf or 680uf (micro farads). Capacitors used in high frequency RF applications can be as small as 1pf (pico farad). The farad is a measure of capacitance (or storage capacity). They are often used in filtering applications, coupling or decoupling applications, or AC-DC smooting applications (there are some large caps in your standard AC-DC power supply that acts to smooth out the ripple on the line).
Super capacitors can be used in solar power applications, battery back-up applications, battery applications, flash-light applications, etc. Aside from the fact that the super capacitor can be charged very quickly due to their low internal resistance, which is known as ESR, but they can just as quickly be discharged. Batteries contain harmful chemicals, and die over time. If you handle your super capacitors carefully, you will die before they do...Seriously! Howver, there are rules...
Super capacitors do not give off gas like lead acid batteries, but they cannot store as much power either. You can place capacitors in series or in parallel to either up the maximum charge voltage, or total capacitorance. We will talk about this later.
Really, there is a lot to be said about capacitors, and you're not going to want to spend your entire day listing to me, so let's get down to the basics. You can go fourth and choose which tabs you;re interested in.
Capacitances: Capacitors Vs. Super capacitors
Have you ever heard someone talk about nano this or micro that? These terms can be used for voltage, power, current, resistance, inductance, etc. When we talk about the capacitance of a capacitor, we will do the same. The below explanation will also help you to understand just how much capacity a super capacitor has in relation to a standard capacitor.
Understanding Capacitance Terminology
1pf (pico farad) = 0.000000000001 farads
1nf (nano farad) = 0.000000001 farads
1uf (micro farad) = 0.000001 farads
1mf (milli farad) = 0.001 farads
The table in the image is much more detailed. This page is an attempt to demonstrate just how much capacity a super capacitor has. A one farad super capacitor can store one million time more energy at a common voltage, than a 1uf capacitor, one billion times more than a 1nf capacitor, and one trillion times more than a 1pf capacitor. Cool, huh?
However, super capacitors have very small voltage ratings, such as 2.5v, 2.7v and 5.5v (Some common values). This makes things difficult, as in order to make our capacitors capable of charging up to a higher voltage, we need to place them in series, which brings a bunch of other variables into play. There are sections coming up on Series/Parallel configurations, as well as charging methods, and balancing methods.
You can also employ DC-DC voltage boosters. Typical DC-DC boosters take a voltage of around 3.4-5VDC and are capable of boosting the output voltage.






 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!